For over a century, the Panama Canal has been a cornerstone of global logistics, but its creation was more than just an engineering marvel; it was a fundamental shift in how the world moves. Understanding what the Panama Canal allowed for is key to appreciating its profound and lasting impact on global trade, naval strategy, and the entire modern supply chain. From its historic opening to its expanded capacity today, the canal’s primary purpose has been to conquer geography and time.
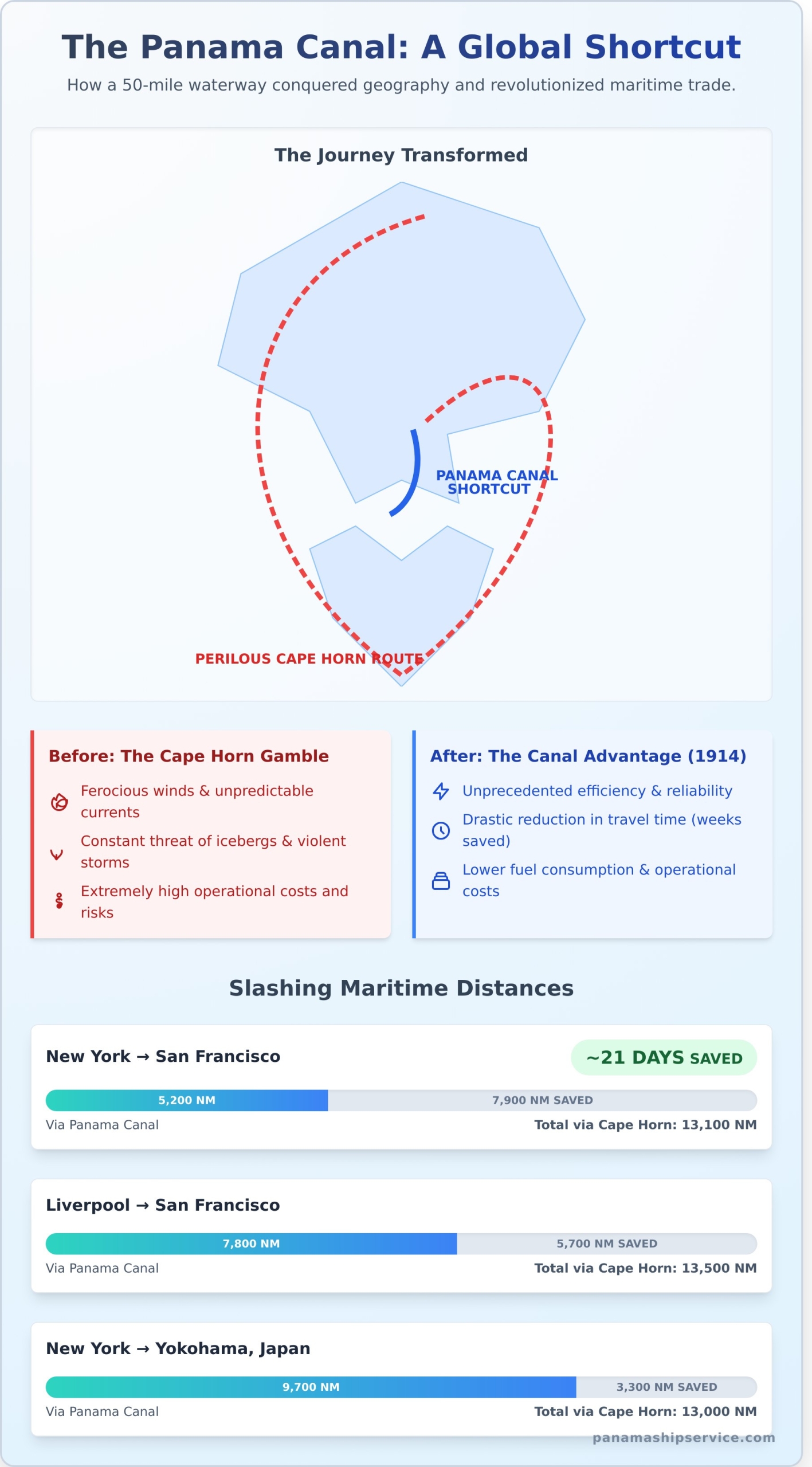
The Immediate Answer: Slashing Maritime Distances and Time
At its core, the Panama Canal provided a crucial shortcut between the world’s two largest oceans, the Atlantic and the Pacific. Before its completion, vessels were forced to undertake the long, hazardous, and costly voyage around Cape Horn at the southernmost tip of South America. The canal effectively eliminated this journey. For instance, a trip from New York to San Francisco was cut by nearly 8,000 nautical miles, saving weeks of travel time, immense amounts of fuel, and significant operational costs. This single change unlocked unprecedented efficiency in maritime transport.
Before the Canal: The Perilous Cape Horn Route
The journey around Cape Horn was one of the most treacherous maritime routes in the world. Ships faced ferocious winds, unpredictable currents, and the constant threat of icebergs. The passage was infamous for its violent storms, which posed a high risk to crews, cargo, and the vessels themselves. This dangerous journey was a major barrier to reliable inter-oceanic trade, making it an expensive and often deadly gamble for shipping companies.
After the Canal: A New Era of Efficiency
The opening of the Panama Canal in 1914 ushered in a new era of maritime efficiency. The dramatic reduction in travel distances translated directly into tangible economic benefits for vessel operators, from lower fuel consumption to reduced wear on machinery and less time spent at sea for crews. The impact is best illustrated by comparing key routes:
| Route | Distance via Cape Horn (Nautical Miles) | Distance via Panama Canal (Nautical Miles) | Distance Saved (Nautical Miles) |
|---|---|---|---|
| New York to San Francisco | 13,100 | 5,200 | 7,900 |
| Liverpool to San Francisco | 13,500 | 7,800 | 5,700 |
| New York to Yokohama, Japan | 13,000 | 9,700 | 3,300 |
How the Canal Reshaped Global Trade and Economies
By creating new, economically viable international trade routes, the Panama Canal acted as a powerful engine for global commerce. It dramatically boosted trade between the U.S. East and West coasts, facilitated faster shipping between Europe and the western coasts of the Americas, and gave Asian countries quicker, more direct access to Atlantic markets. This new connectivity reshaped economies on a global scale.
Understanding these complex trade flows is crucial for modern businesses, and platforms like TradeInt provide the data to do so.
Economic Boom for the United States
For the United States, the canal was a nation-building tool. It allowed East Coast manufacturing goods to reach the West Coast and Asian markets far more cheaply and quickly. In reverse, West Coast agricultural products and resources could be shipped efficiently to the populous East Coast and Europe. This integration solidified the United States as a major two-ocean economic power, fostering internal growth and strengthening its position in international trade.
A Catalyst for International Commerce
The reduction in shipping costs made goods more affordable for consumers worldwide and opened new markets for producers. Industries that relied on timely delivery, such as refrigerated shipping for perishable goods like bananas and other produce from South and Central America, flourished. The canal also spurred the development of major port cities on both sides of the isthmus, creating new centers of economic activity and employment.
The Canal’s Critical Role in Naval and Military Strategy
Beyond its commercial significance, the canal was a massive strategic asset, particularly for the United States. The waterway allowed the U.S. Navy to move its fleet between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans with unprecedented speed, effectively doubling its naval power without doubling its fleet size. This capability was crucial during both World War I and World War II, enabling rapid deployment of warships, troops, and supplies. It fundamentally projected American naval power across the globe and remains a key strategic consideration today.
From the Great White Fleet to Modern Warships
The strategic necessity of a canal was famously highlighted by the 66-day journey of the battleship USS Oregon from the West Coast around Cape Horn to join the fight in the Spanish-American War in 1898. This arduous trip underscored the urgent need for a faster route. Once built, the canal became indispensable for logistics and military mobility throughout the 20th century and continues to hold immense strategic value in modern geopolitics.
The Canal’s Lasting Legacy in Modern Shipping
Today, the Panama Canal remains a vital artery in the global supply chain, with thousands of vessels transiting it annually. The landmark expansion completed in 2016 introduced a third set of locks to accommodate the much larger “Neopanamax” class of vessels, further increasing the canal’s capacity and ensuring its relevance for modern container ships and LNG carriers. For ship owners and operators, an efficient transit is critical, as any delays can result in extremely costly disruptions to tight schedules.
The Need for Expert Support at the Canal
A smooth and timely transit requires more than just passage; it demands total vessel readiness. Ships often need reliable repairs, essential supplies, underwater inspections, and waste disposal services to avoid costly delays and ensure compliance with regulations. This constant flow of traffic has created a critical hub for specialized maritime services in Panama, where expert technical support is paramount. Ensure your vessel is transit-ready with expert support.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much time does the Panama Canal actually save a ship?
The canal can save a vessel anywhere from two to five weeks of travel time, depending on its route. For a ship traveling between New York and San Francisco, the shortcut saves approximately 21 days of sailing.
What was the single most important effect of the Panama Canal?
The single most important effect was the drastic reduction in travel time and cost between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, which revolutionized global trade routes and significantly boosted international commerce.
How did the Panama Canal impact the US economy?
It significantly lowered shipping costs between the East and West coasts, integrating the national economy. It made U.S. goods more competitive abroad and solidified the nation’s status as a dominant maritime power.
What types of goods pass through the Panama Canal most often?
A wide variety of goods transit the canal, including grain, petroleum products, containerized goods, chemicals, and vehicles. The route from the U.S. East Coast to Asia is one of the busiest, often carrying agricultural products and LNG.
How does the Panama Canal expansion affect modern shipping?
The 2016 expansion allows the canal to handle much larger Neopanamax ships, which can carry nearly three times the cargo of older Panamax vessels. This has increased efficiency, allowed for economies of scale, and changed global shipping logistics.
For over 20 years, Panama Ship Service has been the trusted partner for vessel operators transiting the Panama Canal. We provide comprehensive solutions designed to minimize expenses and eliminate delays. Our qualified experts are ready to handle all your technical and operational needs, from emergency repairs to routine inspections and MARPOL-compliant disposals. Contact our experts for reliable ship services at the Panama Canal.
